Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils; these are two round lumps of flesh at the back of the throat. A tonsil is a Lymphoid tissue and its major activity of barrier to prevent any pathogen from penetrating the body. However, if they become enlarged, they lead to pain, difficulty in swallowing and other conditions that hinder the operations of a human being.
In this article, we will learn about the causes of tonsillitis, the signs and treatment, and distinctions of several types of this sickness.
What is Tonsillitis?
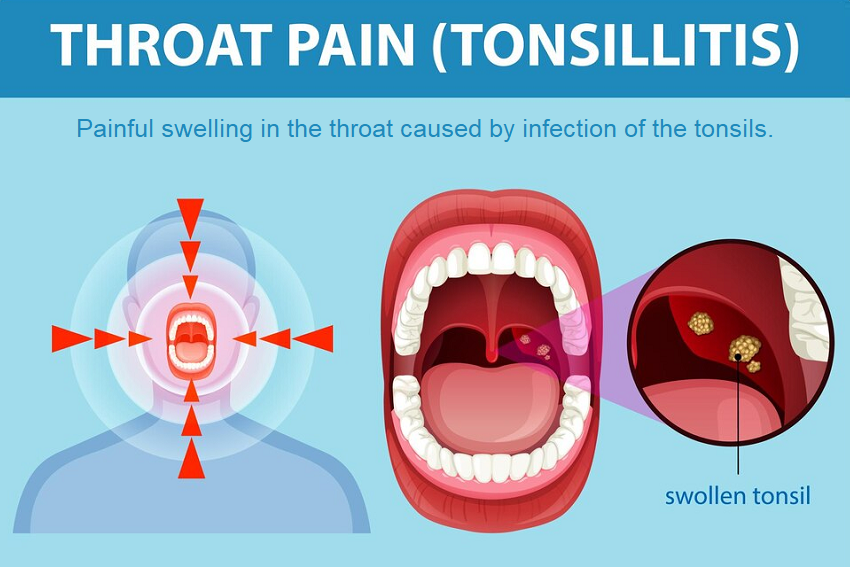
Tonsillitis is defined as an inflammation of the tonsils prompted by bacterial or viral infection which causes many signs. It is an illness, which is not very rare, often observed in children, yet they can be of almost any age; there are several types of the disease – viral, bacterial and so on.
Types of tonsillitis
Acute Tonsillitis:
Usually acute tonsillitis is not fatal, the most common cause is viral or bacterial infection and its type is usually acute. Typically, rubella manifests mild acute symptoms such as sore throat, difficulty in swallowing food, fever, headache, and swollen cervical lymph nodes. At times, a bacterial infection may manifest symptoms that are more serious than viral infections or digestive issues, including breathing problems and skin rash.
Chronic Tonsillitis:
This condition is recurrent tonsillitis stands for the infection of the tonsils that occurs at a low severity. SMR tonsillitis alone could lead to long-standing sore throat, stinking breath, and swollen tonsils. Often it is result of either bacterial or viral infection or it could be allergic to some organism or particles. There are many complications of tonsillitis chronica, including sleep apnea, or abscesses at the tonsil area.
Recurrent Tonsillitis:
This condition is a type of recurrent tonsillitis, which is an inflammation of the tonsils that is normally not serious. Even the SMR tonsillitis might lead to chronic sore throat, bad breath from our mouth, and enlarged tonsils. Most often it is caused by Bacterial or viral infection or may be due to Allergy to an organism or particle. Tonsillitis chronica can become other diseases as for example sleep apnea or abscesses at the tonsils.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is a common inflammation disease of tonsils which are two small oval shaped glandlike structures in the throat. It is mostly due to a virus or bacteria and all the symptoms include sore throat, swallowing problems, fever, and swollen neck glands. Now, let us take a closer look at factors that cause tonsillitis to happen to occur.
Viral Causes:
Tonsillitis can be caused by several different viruses, some of which include:
- Adenovirus: This is a group of viruses that cause flu like illnesses including the common cold such as tonsillitis. In addition, adenoviruses are known to trigger tonsillitis and other related symptoms such as coughing and a runny nose. Adenoviruses spread directly through contact with an adenovirus infected person or indirectly by physical contact with an object infected with the virus.
- Influenza Virus: Some of these diseases include the influenza virus; this also causes tonsillitis. Flu illnesses may result in very bad tonsillitis with fever and muscle pain, chills. This is spread by particles in the air and passes through the air each time the affected people cough or sneeze and is a seasonal disease-Most often flu is associated with the winter season.
- Epstein-Barr Virus: Infectious mononucleosis, usually referred to as mono is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Mono might cause tonsilitis and symptoms are like any other disease: fatigue, sign of enlarged lymph gland and sore throat. Mono may also be acquired through direct contact with droplets released through the individual’s respiratory system just like influenza.
- Herpes Simplex Virus: The exact cause of the tonsillitis they named it herpes tonsillitis and the cause is the herpes simplex virus. This is a type of tonsillitis that is favorite among children and it is characterized by sore throat, ulcers on the tonsils and fever, swollen lymph nodes. Herpes tonsillitis can spread from an infected person’s saliva, or even touching objects that have the said saliva on them.
Bacterial Causes:
Other causes of tonsillitis are nonviral and include those caused by bacteria within the area such as peritonsillar abscess. Some of the common bacteria responsible for this condition are:
- Streptococcus pyogenes: It is widely acknowledged that this bacterium is the main autological agent of bacterial tonsillitis. This is the infection that will make the diseased person have throat soreness, inflamed tonsils, and even formation of white patches at the back of throat. S pyogenes is through droplet infection or by coming into contact with saliva from affected patients. If left untreated it leads to inflammation of the kidney or rheumatic fever.
- Haemophilus influenzae: This bacterium appears to be called this because it might be associated with the flu virus, yet it is not the same. Acute bacterial tonsillitis in children is occasionally caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Other signs include cough, bad sore throat, high fever, and inflamed tonsils are other signs known that come with the infection. It can be passed through the air as droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes or through contact with their saliva.
Other Contributing Factors
- The client’s exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke or pollution.
- This condition results in the existence of chronic throat inflammation since individuals suffering from allergies.
- This disappeared immune systems means that people get infected easily.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
Some signs of tonsillitis include sore throat, troubles swallowing, headaches, temperature and earache and swollen glands. Most children only develop throat inflammation but there are other severe effects if affected by the virus.
Common Symptoms
- Sore Throat.
- Swollen Tonsils.
- Difficulty Swallowing.
- Fever.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes.
Additional Symptoms
- Bad breath (halitosis).
- Hoarseness or loss of voice.
- Headache and fatigue.
- Ear pain due to referred pain from the throat.
Symptoms in Severe Cases
- Difficulty breathing due to obstructed airways.
- Persistent high fever.
- Dehydration from difficulty swallowing fluids.
- Pus-filled pockets (abscesses) around the tonsils, known as peritonsillar abscesses.
Diagnosing Tonsillitis
In order to ascertain if it is viral or bacterial, proper diagnosis must be conducted in the case of tonsillitis. This distinction guides the treatment plan.
Physical Examination
- Feeling for nodal enlargement and looking at the throat for signs of redness, inflammation, and white lesions.
- The next procedure that is done is feeling the throat and neck for any swell up of the lymph nodes.
Laboratory Tests
- Throat Culture: A throat test with a swab to test for bacterial infection like strep throat from the back of throat.
- Rapid Strep Test: provides a quick test to confirm groups A streptococcus.
- Blood Tests: Where generalized or chronic tonsillitis is suspected, it is possible to carry out blood tests in a bid to diagnose other diseases such as mononucleosis.
Treatment Options for Tonsillitis
The Treatment of tonsillitis as well depends on its cause and the severity of the symptoms. Most viral infections are cured by the body on its own as opposed to bacterial infections which often have to be treated by anti-bacterial medications. Of course, not all causes of this disease require operations:
Home Care and Remedies
For mild cases of tonsillitis, supportive care can alleviate symptoms:
- Rest: In most cases people are told to remain idle so that the body can take its normal course in fighting the disease and healing.
- Stay hydrated: For the symptom treatment you could take water, warm tea, or even cold take since this would ease the throat and hydrate you.
- Gargle: It is much easier to treat throat pains and inflammation through warm gargling with water added to salt.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: For pain relief and reducing fever we may take analgesic containing drugs – paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
- Humidifier: You can reduce the symptoms because when using the humidifier, you are increasing the level of moisture in the air hence reducing throat irritation.
- Lozenges or hard candy: These can help in sooth the throat and reduce the thickness of the secretion.
Medications
- Antibiotics: In case of bacterial tonsillitis, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to get rid of the bacteria causing the infection in your system. The antibiotics administered are not prescribed strictly, and they are not even stopped even when there is some improvement noted on the usage of the medicine.
- Viral infections: Just like bacterial infections, viral infections do not respond to antibiotics but when the affected individual takes some pain relievers and has enough rest, the problem will soon be solved.
Surgical Treatment: Tonsillectomy
When tonsillitis is frequent, long-lasting, or severe, surgical procedure of their removal – tonsillectomy – is still a possibility. This work entails the operative excision of tonsils with the intent to have a more joyful result that would discourage any possibility of infections or manifestations of disease in the future.
It can be caused by electrodesiccation, laser tonsillectomy or the cold knife procedure. Tonsillectomy patients may only be sore, swollen or bleed lightly for several days, but it might take up to three weeks to in general.
Post-Surgery Care
As a patient’s precaution after operation, the patients should adhere to the doctor’s advice on how to superintend after the tonsillectomy. This may include:
- Pain management: Some discomfort that may arise after the procedure is treated by taking over the counter medications such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Hydration: They took cocktail when they took alcohol, lots of fluids needed to be had to gain faster.
- Diet: The diet starts with clear liquids, transition diet from a soft diet and then regular diet can be taken.
- Rest: Rest isn’t just about feeling refreshed—it’s when your body gets to work repairing itself. During rest, your muscles, bones, and organs have the time they need to heal and recover from daily wear and tear or physical exertion. It’s like giving your body a chance to recharge.
- Avoid physical activity: Avoid physical exertion and exercises in general, for about two weeks after the procedure.
- Prevent infection: A rule of thumb is to stay away from people with colds or flu at least until the recovery is complete.
Preventing Tonsillitis
While it’s not always possible to prevent tonsillitis, certain measures can reduce the risk:
Hygiene Practices
- Wash your hands often—it’s one of the easiest ways to stop germs in their tracks.
- Avoid close contact with people who are coughing, sneezing, or sick.
- Cover your sneezes and coughs with a tissue or your elbow (and toss that tissue right away).
Lifestyle Habits
- Eat a balanced, nutritious diet to keep your immune system strong.
- Drink plenty of water and make sure you’re getting enough rest each night.
- Stay away from irritants like cigarette smoke and polluted air—they can make things worse for your throat and lungs.
Vaccination
Certain vaccines, such as the flu vaccine, can help prevent infections that may lead to tonsillitis.
Complications of Tonsillitis
If left untreated, or if it becomes severe, tonsillitis can lead to complications that may need urgent medical attention. Here are a few examples:
Common Complications
- Peritonsillar Abscess: A severe sequel of tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess is formed by infected tissues around the tonsils, and presents with pain, dysphagia, and fever.
- Middle Ear Infections: Tonsillitis may cause other infections such as middle ear infection in children which leads to ear pain, fever, and poor hearing.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: They may also become infected and get enlarged causing tonsillitis and sleep apnea where breathing during sleep is interrupted.
Also Read – Why Sleep Timing Matters: The Science of Sleep
Rare but Serious Complications
- Rheumatic Fever: An acute sequel of untreated streptococcal tonsillitis, rheumatic fever causes inflammation and stenosis of the cardiac valves, which could culminate in heart failure if left untreated.
- Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: This complication may develop after a streptococcal infection that damages the kidneys and leads to swelling, blood in urine, and high blood pressure.
Conclusion
Tonsillitis is a common illness that affects the tonsils – round shaped formations located at the back of the throat. In fact, this disease is not unique to children only, adults are also at risk of developing this disease through bacterial or viral infection. There is fever, sore throat, difficulty in swallowing and I also experienced swollen tonsils. If not tackled, tonsillitis is likely to cause peritonsillar abscesses or repeat infections.
The management of this type of sickness normally involves sorting out the cause of the tonsillitis – bacterial or viral. Antibacterial may be used to treat bacterial infections while viral infections are treated by a lot of bed rest and the use of paracetamol. In cases where the tonsillitis infection is frequent or severe, your doctor may recommend a tonsillectomy — the removal of the tonsils. Thus, students, individuals’ awareness of tonsillitis: etiology, signs, and management will help them receive proper treatment.