One thing is constant in the dynamic world of digital marketing: speed matters. Page speed optimization has become a critical component of technical SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) that may make or break a website’s online visibility. The significance of optimizing web page loading time cannot be understated as the digital sphere becomes more competitive.
Consider the following scenario: You discover a website that seems promising, with useful content and a visually pleasing layout. However, the page loads incredibly slowly when you click on a link to obtain further information. You hit the “back” button out of frustration and never look back. Just this typical user experience is what page speed optimization seeks to solve. We will explore the nuances of page speed optimization in this article, as well as why it is crucial for Technical SEO.
The Digital Landscape: A Need for Speed
The speed of the digital world is unreal. User expectations are higher than ever in a time when information is readily available. If sites take more than three seconds to load, 53% of mobile site visits are abandoned, per Google’s research. Additionally, research by Akamai found that a one-second delay in page load time might lead to a 7% decrease in conversions.
These statistics demonstrate the impatience of online users as well as the direct relationship between page loading speed and user behavior. Success in the digital arena depends on meeting these requirements, therefore page speed optimization is important.
What is Page Speed Optimization?
In the world of web development and SEO, page speed optimization is the methodical process of improving the speed at which online pages load. In order to shorten the time it takes for a user to fully load a website’s pages, a number of technical solutions and fine-tuning approaches are used.
This optimization has a big impact on search engine rankings since quicker-loading websites are given priority by search engines like Google. It also enhances user experience by delivering faster and more responsive web content. Page speed optimization covers a range of topics, including server performance, browser caching, image optimization, code efficiency, and more, all with the goal of giving users a smoother and faster web experience.
The User Experience: A Make or Break Factor
The success of a website is increasingly dependent on the user experience (UX). It addresses a variety of subjects, including page loading speed and accessibility as well as navigation and design. The following are some key reasons why enhancing page speed is necessary for delivering exceptional user experiences:
Decreases in bounce rates
A website that loads slowly will inevitably lose visitors. Users are more inclined to leave a website and explore for alternatives when the page loads slowly. Search engines interpret high bounce rates as a sign of poor content or user experience, which can have a negative impact on a website’s search engine rankings.
Enhanced Participation
Users are more engaged when pages load more quickly. Visitors are more inclined to stick around, browse other sites, and engage with the content if they can get the information they need fast. This prolonged interaction may have a favorable effect on measures like time on site and page views, signaling to search engines that the website has worthwhile material.
Better Conversion Rates
Conversion rates and page speed have a well-established relationship. More visitors convert to websites that load quickly. A more user-friendly online experience motivates visitors to take action, whether it’s completing a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or submitting a contact form.
SEO Implications: Speed as a Ranking Factor
The greatest outcomes for users are what search engines are motivated to provide. When deciding search ranks, they take a lot of things into account to do this. Increasingly important as a ranking element in recent years, is page speed. Here are some reasons why speed counts in the SEO industry:
Google’s Focus on Speed
The most popular search engine, Google, has long-supported websites that load quickly. Google declared that page speed would affect search results in 2010. Webmasters and SEO specialists received a clear message from this announcement: page performance optimization needs to be prioritized if you want to rank well on Google.
Indexing for mobile first
Google launched mobile-first indexing as the popularity of mobile web browsing grew. This indicates that Google ranks and indexes material mostly using its mobile version. Page performance is even more important in this mobile-first era because slower-loading sites can lead to a poor user experience on mobile devices.
Core Web Vitals
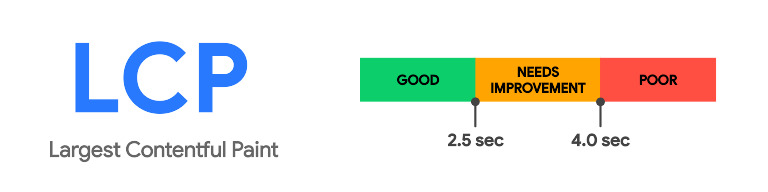
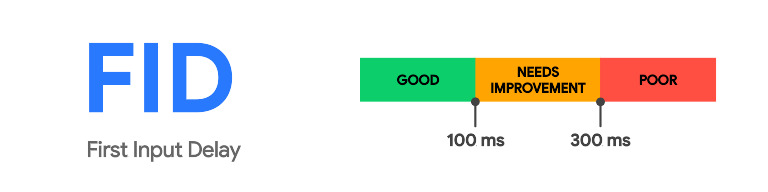
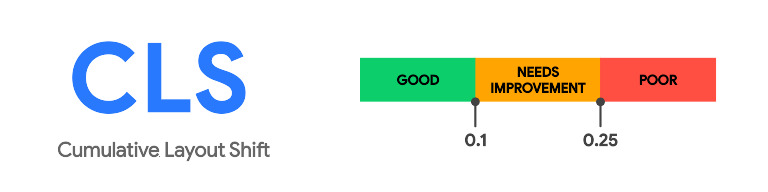
Google introduced Core Web Vitals, a set of user-focused metrics that assess the overall web page experience, including page speed, in May 2021. These metrics include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Websites that excel in these areas are more likely to receive favorable rankings in Google’s search results.
Page Speed Optimization and SEO
Technical SEO is optimizing a website’s technical components to raise its search engine visibility. Page speed optimization is a key aspect of technical SEO even though it covers a wide variety of variables. Here is how improving page performance fits into the bigger picture of technical SEO:
Crawl Efficiency
Search engine bots, like Google’s crawler, regularly visit websites to index their content. A faster-loading website enables these bots to crawl more efficiently, ensuring that all pages and content are properly indexed. When a website is slow to load, search engine crawlers may not be able to access all of its pages, leading to incomplete indexing and potential SEO issues.
Enhanced indexation
A well-optimized website with quick-loading pages is more likely to get its information indexed quickly and correctly. This is essential to ensure that the pages of your website show up in search engine results for pertinent queries. Better visibility and more organic traffic can result from improved indexation.
Less Duplicate Content
Duplicate content problems are more likely to occur on slow-loading websites. Users can click more than once when a website loads slowly, which sends numerous requests to the server. This might result in duplicate content problems because search engines would index numerous copies of the same page. By enhancing user experience, page speed optimization can help reduce these issues. You can use plagiarism checker to identify duplicate content on your page.
The Art of Increasing Page Speed
A methodical strategy that takes into account many technical aspects is necessary to achieve optimal page loading times. Let’s look at a few of the main elements of page performance optimization:
Client Performance
A website’s page speed is significantly influenced by the web server’s performance. In order for servers to effectively handle incoming requests, webmasters and hosting companies must make sure they are properly set. Software, hardware, and network infrastructure optimization for servers may be necessary.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A potent instrument in the fight for quicker page loads is the Content Delivery Network (CDN). Website material is distributed through CDNs to servers positioned strategically all over the world. The CDN uses the server that is nearest to the user’s location to serve content when they browse a website, lowering latency and load times.
Caching in the browser
Images, stylesheets, and scripts can all be kept locally on a user’s device thanks to browser caching. The browser can access these resources from the cache rather than making a new request to the server when a user returns to the website. This considerably lowers server load and page load times. You can try this cahing plugins to speed up your WordPress website.
Image Enhancement
One of the components that weigh the most on a web page is frequently an image. When reducing photos without sacrificing quality, contemporary image formats like WebP are used. Image optimization lowers the amount of data that must be delivered, resulting in quicker page loads.
Compression and Mining
Codes like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that are minified have their extraneous characters and whitespace removed. Further reducing file sizes are compression methods like Gzip. Smaller file sizes lead to quicker downloads and quicker page loads.
Important Rendering Path
The series of actions a browser takes to render a web page is known as the critical rendering path. Prioritizing the loading of vital resources, like the primary content, over optional components is one way to optimize the critical rendering path. Users will see relevant content as soon as possible thanks to this.
Efficacy of the Code
For improving page speed, well-organized, effective code is essential. A website’s performance may suffer from bloated or poorly written code. Clean, effective code that minimizes pointless operations and lessens server load should be the goal of all web developers.
Measuring and Monitoring Page Speed
To effectively optimize page speed, webmasters and SEO professionals must rely on accurate measurement and continuous monitoring. Several tools and metrics are available for assessing page speed performance:
Page Speed Evaluation
An effective tool for evaluating page speed efficacy is Google’s PageSpeed Insights. It provides a complete analysis of a webpage’s loading speed on desktop and mobile devices. A rating and comprehensive improvement advice are provided by PageSpeed Insights.
Lighthouse
Web page performance auditing extension called Lighthouse is free to use. Page load times, accessibility, and best practices are just a few of the performance-related insights it offers. It is possible to utilize Lighthouse as a standalone tool or as part of web browsers.
Web Vitals
As already noted, Google’s Core Web Vitals are a set of measures that focus on the user to assess how well a webpage meets their needs. These measurements — which include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)— provide a comprehensive picture of page speed and user experience.
Real User Monitoring
Tracking and examining actual user experiences on websites is known as real user monitoring. RUM tools record information on how actual users interact with a website, such as page load speeds, device types, and geographic locations. Ongoing optimization attempts may be guided by this data.
The Mobile Obstacle
Page speed optimization is a particularly difficult task as mobile devices increasingly replace desktop computers as the major method of internet access. Mobile customers, who frequently have slower connections, have greater standards for quick page loads. Here is how page performance optimization changes to accommodate the mobile environment:
Mobile-Friendly Design
A website’s ability to adapt to various screen sizes and devices is ensured by responsive web design. Giving mobile consumers a consistent and quick-loading experience requires the implementation of responsive design concepts.
Mobile-First Optimization
Given Google’s mobile-first indexing, websites should prioritize mobile optimization. This includes optimizing images and content for mobile devices, reducing unnecessary scripts, and ensuring that mobile users have a fast-loading experience.
Accelerated Mobile Pages
The open-source project Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) attempts to give mobile web pages blazingly quick loading times. Webmasters can design mobile-optimized pages that load almost instantly by following the AMP requirements, meeting the expectations of mobile visitors.
User-Centric Approach
Page speed optimization is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. To succeed, it must be approached with a user-centric mindset. Here are some strategies that prioritize the user’s experience:
Tests with Users
An effective way to learn how actual people feel about a website’s speed is to conduct user testing. Users’ comments can point out problems and potential areas for development that technical analysis by itself might not be able to reveal.
B/N Testing
A/B testing entails contrasting two iterations of a web page to see which one performs better in terms of page speed and other metrics. Webmasters can improve their optimization efforts based on actual user data by using this iterative methodology.
Prioritizing Above-the-Fold Content
Above-the-fold content refers to the portion of a web page that is visible without scrolling. Prioritizing the loading of critical above-the-fold content ensures that users see meaningful information immediately, even if the rest of the page is still loading.
The Effects of Outside Scripts
A lot of websites rely on third-party scripts and integrations to offer extra features like social media widgets, analytics, and advertising. These scripts can improve user experience, but they can also severely slow down pages.
When using third-party scripts, webmasters must balance performance and functionality. Taking into account the following:
Script Consolidation
Consolidating multiple third-party scripts into a single script or loading them asynchronously can reduce the impact on page speed. Minimizing the number of external requests can lead to faster load times.
Inefficient loading
Lazy loading is a strategy that defers the loading of specific resources, like photos or videos, until they are displayed in the user’s viewport. This can speed up initial page loads while maintaining a seamless user experience.
Regular Auditing
Regularly auditing and reviewing the third-party scripts used on a website is essential. Remove any scripts that are no longer needed or causing performance issues. Additionally, consider the impact of new scripts before implementing them.
Continued Speed-Seeking
Increasing page speed is a continuous activity, not a one-time task. The elements affecting page speed are dynamic in the digital world and are subject to change. The desire for speed necessitates that webmasters and SEO specialists be alert and flexible. To maintain the ideal page speed, try the following tactics:
Continuous Monitoring
Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and real user monitoring. Pay attention to changes in performance metrics and address any issues promptly.
Periodic Audits
Conduct recurring audits of the scripts, content, and code on your website. Find ways to enhance page speed even more and the user experience as a whole.
Keep yourself informed.
Keep abreast of business developments and page-speed optimization best practices. Page speed may be affected by search engine algorithm updates and the emergence of new technology.
Speculate and iterate
To find areas for improvement, keep running A/B and user tests. Implement modifications in response to data and user feedback, then retest to assess the effects.
Conclusion
In the digital world, when success is equated with quickness, optimizing for page performance is crucial. For webmasters, SEO experts, and organizations looking to succeed online, it is not just a technical task but also a strategic necessity. Websites can provide outstanding user experiences, lower bounce rates, and boost conversion rates by placing a high priority on page speed.
In addition, speed is a key component of successful Technical SEO because search engines like Google reward it with higher rankings. The goal of speed is a never-ending adventure as we negotiate the always changing digital environment; it promises better visibility, greater engagement, and a competitive edge online.