Core Web Vitals is a set of specific website performance metrics introduced by Google to measure and evaluate the user experience of a webpage. These metrics impact the core rankings and mainly focus on three key aspects of user experience: Interactivity, Visual Stability, and Loading.
When discussing the Google core web vitals importance, it’s vital to understand that they are part of Google’s broader initiative to prioritize the user experience in their search rankings. This is known as the Google page experience update.
Google uses these CWV metrics as part of its search algorithm to rank websites based on their page experience. Websites that provide a better UX by scoring well on these metrics may receive higher core rankings in Google’s search results compared to those with poorer scores.
3 Key Metrics of Core Web Vitals
- First Input Delay (FID): FID measures the time delay between a user’s first interaction (e.g., clicking a link or button) and the website’s response to that interaction. A low FID score indicates that the website is responsive and interactive.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS measures the number of unexpected layout shifts that occur during the page’s loading process. A high CLS score means elements on the page move around, causing frustration for users. A low CLS score ensures visual stability during the loading process.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric measures the time it takes for the main content of a webpage to load and become visible to the user. A good LCP score indicates the website loads quickly, providing a better user experience.
Improving Core Web Vitals with time is essential and often requires technical adjustments to the website’s code and its overall performance optimization. Web developers with expertise in core web vitals and SEO can help enhance a site to meet Google’s page experience benchmarks.
Understand Core Web Vitals
Let’s understand the importance of these core web vitals and how they impact the new ranking factors in SEO:
First Input Delay (FID)
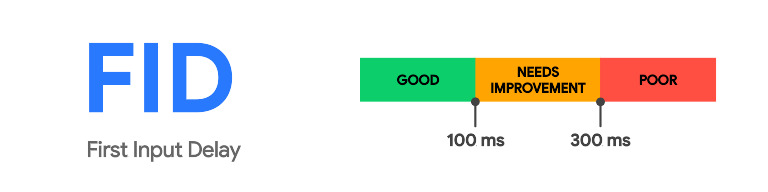
First Input Delay is a core web vitals ranking factor that measures the responsiveness of a webpage to user interactions. It quantifies the delay between a user initiating an action (such as clicking a button or a link) and the browser’s response to that action. A low FID is crucial for ensuring users can interact with the website without experiencing frustrating delays.
Google considers the following time ranges for FID scores:
- Good: FID is 100 milliseconds or less.
- Needs Improvement: FID ranges from 100 milliseconds to 300 milliseconds.
- Poor: FID exceeds 300 milliseconds.
To enhance FID and optimize user interactions, consider the following strategies:
- Minimize JavaScript execution time by eliminating unnecessary code.
- Use web workers to offload non-essential tasks from the main thread, allowing it to focus on user interactions.
- Defer non-essential JavaScript until after the initial rendering to ensure the main thread is available for user interaction.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
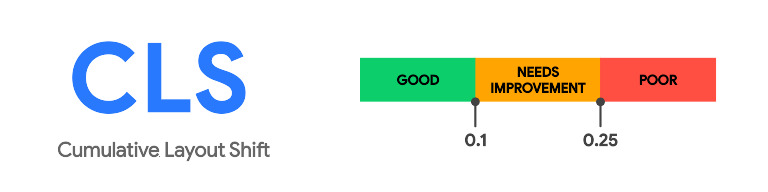
Cumulative Layout Shift measures the visual stability of a webpage during its loading process. It quantifies how much the page’s elements shift around unexpectedly, potentially causing confusion or frustration for users. CLS is essential to maintain a smooth and enjoyable user experience, especially when elements like images or ads load after the initial content.
Google considers the following thresholds for CLS scores:
- Good: CLS is 0.1 or less.
- Needs Improvement: CLS ranges from 0.1 to 0.25.
- Poor: CLS exceeds 0.25.
Consider the following techniques to reduce Cumulative Layout Shift:
- Always set dimensions for media elements like images and videos.
- Avoid inserting content above existing content, as this can push elements down and cause unexpected and untimely shifts.
- Load and initialize ads and iframes with proper size attributes to prevent unexpected layout disruptions.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
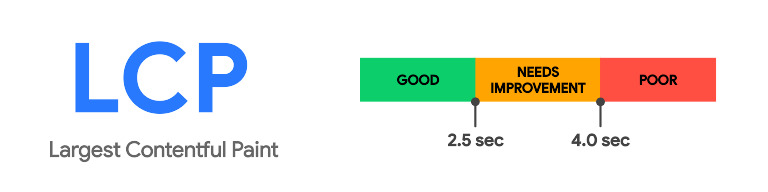
Largest Contentful Paint measures the loading speed of the largest element, or “contentful paint,” on a webpage. The contentful paint is usually an image, video, or large block of text that is essential for the user to understand the page’s content. LCP is crucial because it reflects how quickly the main content becomes visible to users.
Google considers the following time ranges for LCP scores:
- Good: LCP occurs within 2.5 seconds or less.
- Needs Improvement: LCP takes between 2.5 and 4 seconds.
- Poor: LCP exceeds 4 seconds.
To improve LCP, you can employ several optimization techniques, including:
- Optimizing and compressing images to reduce their file sizes.
- Minimizing server response times and leveraging browser caching.
- Prioritizing the loading of critical resources, such as the main content, expedites the rendering process.
Why are Core Web Vitals important?
User Experience Improvement
Core Web Vitals are crucial because they directly relate to the user experience of a website. A fast-loading and responsive website with stable visuals enhances user satisfaction and engagement. When visitors have a positive experience on your site, they are more likely to stay longer, explore more pages, and convert into customers or subscribers.
Google’s Page Experience Update
Google considers user experience an essential ranking factor. Core Web Vitals are now part of Google’s ranking algorithm, which means websites that perform well on these metrics have a higher chance of ranking higher in search results. As a result, optimizing Core Web Vitals can improve your website’s visibility and organic traffic from search engines.
Mobile Friendliness
Core Web Vitals are particularly important for mobile users, as they heavily impact mobile site performance. Since most internet users access the web through mobile devices, providing a smooth and efficient mobile experience is crucial for retaining and attracting users. It’s one of the essential factors that shows the importance of core web vitals and SEO combined.
SEO and Search Rankings
Beyond Core Web Vitals’ direct impact on the page experience update, a better-performing website often correlates with other SEO benefits. Faster-loading sites tend to have lower bounce rates and higher click-through rates, which can indirectly contribute to improved search rankings.
Competitive Advantage
Websites that prioritize user experience and optimize Core Web Vitals can gain a competitive edge. In a highly competitive online landscape, providing a better user experience can set your website apart from competitors and lead to increased customer loyalty. Get the right insights using the SEO report generator tool and plan your strategy accordingly.
Core Web Vitals are essential for creating a positive user experience, improving search rankings, and driving business success. Optimizing these metrics not only benefits website owners but also ensures that users have a better online experience across the web.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals Score?
There are several tools like Search Console, Semrush, AgencyEasy, and Lighthouse that can help you analyze website performance and generate insightful reports that can be used to identify the weaknesses and areas of improvement in your campaign.
Start working on improving the SEO campaigns with core web vitals. Read along to learn how to improve core web vitals scores.
Implement a Caching Solution
Optimizing Core Web Vitals won’t just boost your organic rankings; it also delivers a better user experience that could lead to engaged customers, higher conversion rates, and other advantages. As Google has made user experience an integral ranking factor, optimizing for Core Web Vitals becomes even more essential.
Pagespeed is one of the key web vitals, yet also one of the easiest metrics to improve. In most cases, all that’s necessary to improve Pagespeed is optimizing some basic front-end elements like image optimization or making sure your content renders quickly for all devices. Caching is the practice of temporarily storing pages in memory to speed up their delivery to users. Caching can be particularly effective when serving pages requiring several network requests.
There are various strategies available to you for improving the Core Web Vitals performance of your website. By prioritizing pages that cause trouble and working closely with your web team, substantial gains can be realized quickly. Implementing a caching plugins to your website can significantly improve the overall performance of your website.
Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
When pages load too slowly, visitors may leave quickly – this leads to poor user experiences that result in lost traffic, reduced conversion rates, and possibly lower organic rankings. One of the key components of passing Core Web Vitals is to eliminate render-blocking files and resources. Render-blocking files are files that block browsers from rendering HTML and displaying content above the fold until they finish loading.
Another common issue is script> tags in the body being blocked from rendering content below them, this can be solved by placing them at the bottom of the body> tag with async or defer attributes applied. Optimizing render-blocking means making sure that JS and CSS files are as small as possible while still meeting their functional requirements. Use async and defer attributes to make non-blocking code available and reduce its overall impact on website speed.
Plugins, third-party tools like Google Analytics or Facebook, Pixel, or CMS systems such as WordPress usually add these render-blocking files. Furthermore, sites using excessive JavaScript may struggle with passing Core Web Vitals as their pages require many resources to display correctly. Using the latest tools and techniques to enhance the performance of CWV metrics is vital for a better-performing website.
Use a Content Delivery Network
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help you improve Google Core Web Vitals and SEO results. These essential metrics measure a website’s loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. CDNs can positively impact these metrics by addressing various performance-related factors.
CDNs distribute website assets across multiple servers worldwide, reducing latency and improving loading times, which directly influences the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID) scores. By offloading static content delivery to dedicated CDN servers, the load on the web server decreases, resulting in faster server response times and further enhancing FID metrics. incorporating a CDN into your website’s architecture can lead to substantial improvements in Google Core Web Vitals.
Visitors expect your page to load quickly and be ready for interaction within seconds – this is why Google takes into account Core Web Vitals metrics which gauge user experience. Google measures page loading speeds as an overall good score when they fall within 2.5 seconds, any time over this requires improvement. Google also considers other performance-related metrics, including FCP and TTI.
Defer Loading of JavaScript
Google’s Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that play a part in your search ranking, and optimizing them to create a positive user experience and ensure an effortless conversion process. By eliminating performance barriers, increasing visitors are likely to stay longer and explore more content resulting in greater conversions.
Using deferred loading of JavaScript can significantly improve Google Core Web Vitals by optimizing the loading process of JavaScript resources and enhancing the user experience. By deferring the loading and execution of non-critical JavaScript, web pages can load faster, become interactive more quickly, and provide a smoother user experience. This, in turn, positively impacts Google’s Core Web Vitals, leading to better search engine rankings and more satisfied website visitors.
When JavaScript resources are loaded synchronously, they can block the rendering of the main content on a webpage. By using the “defer” attribute on script tags, you allow the browser to continue parsing and rendering the page while the JavaScript is downloaded in the background. This ensures that the largest content element is displayed to the user quickly, leading to a better LCP score.
Properly Size and Optimize Images
By speeding up page loads, enhancing user experience, and having a beneficial effect on a number of important performance indicators, using appropriately sized and optimized pictures can greatly enhance Google CWV metrics. Google measures page speed and quality using performance factors called Core Web Vitals, which have an impact on your search ranking.
The largest elements on a webpage are frequently images, and if they are not correctly optimized, they might cause the page to load slowly. You may drastically reduce the file size of photographs by shrinking them to fit the screen and compressing them without losing quality. Smaller image sizes mean quicker downloads, leading to faster LCP scores and a better user experience.
Optimizing these technical aspects of your website, optimizing these technical aspects improves overall user experience by making it more responsive to visitor actions. This ultimately results in more effective conversion processes and business results, increasing traffic and revenues to your website and ranking higher on Google searches – in turn, increasing traffic and revenues.
Key Takeaways
Core Web Vitals are essential for creating a positive user experience, improving search rankings, and driving business success. Understanding these metrics and optimizing them not only benefits website owners but also ensures that users have a better online experience across the web. As a result, investing in the best SEO report generator tool for the improvement of Core Web Vitals is a worthwhile endeavor for any website or online business.